Contents
7.22.3 DPP protocol usage
Overview
The DPP protocols are typically exchanged between one pair of devices, where one device takes on the role of Configurator and the other device takes on the role of Enrollee. Either device may initiate the DPP protocol. Roles are assumed by the Initiator and Responder based upon the type of network that DPP is being used to set-up.
Infrastructure setup and connectivity
A Configurator can be used to set up an infrastructure network consisting of one or more APs. A Configurator can set up clients (STA devices) and APs in any order and give each of the devices appropriate configuration information to support subsequent discovery and connectivity to the infrastructure network.
AP configuration
The configuration information provided to an AP may include: Wireless LAN Driver Version 11.0 for Access Point Programming Guide
- The SSID for the BSS
- Fields to be carried in Beacon and Probe Response frames to designate the connectivity policy
- One or more Connectors generated by the Configurator for the authorized connectivity
- An optional WPA2-Personal
- passphrase(s) or PSK(s) for the BSS to support legacy devices
Infrastructure connectivity
- The Configurator provisions both AP and non-AP STA Enrollees to establish a trusted and secure connection.
- To provide a scalable method of enabling new Enrollees to connect to the AP without having to contact the AP each time, the Configurator provisions Connectors on each Enrollee. A Connector is a tuple of a Group Identifier, a Network Role, and a Network Access Key, all signed by the Configurator. The Group Identifier may indicate a specific peer or a wildcard that indicates all peers.
Message flows for infrastructure connectivity
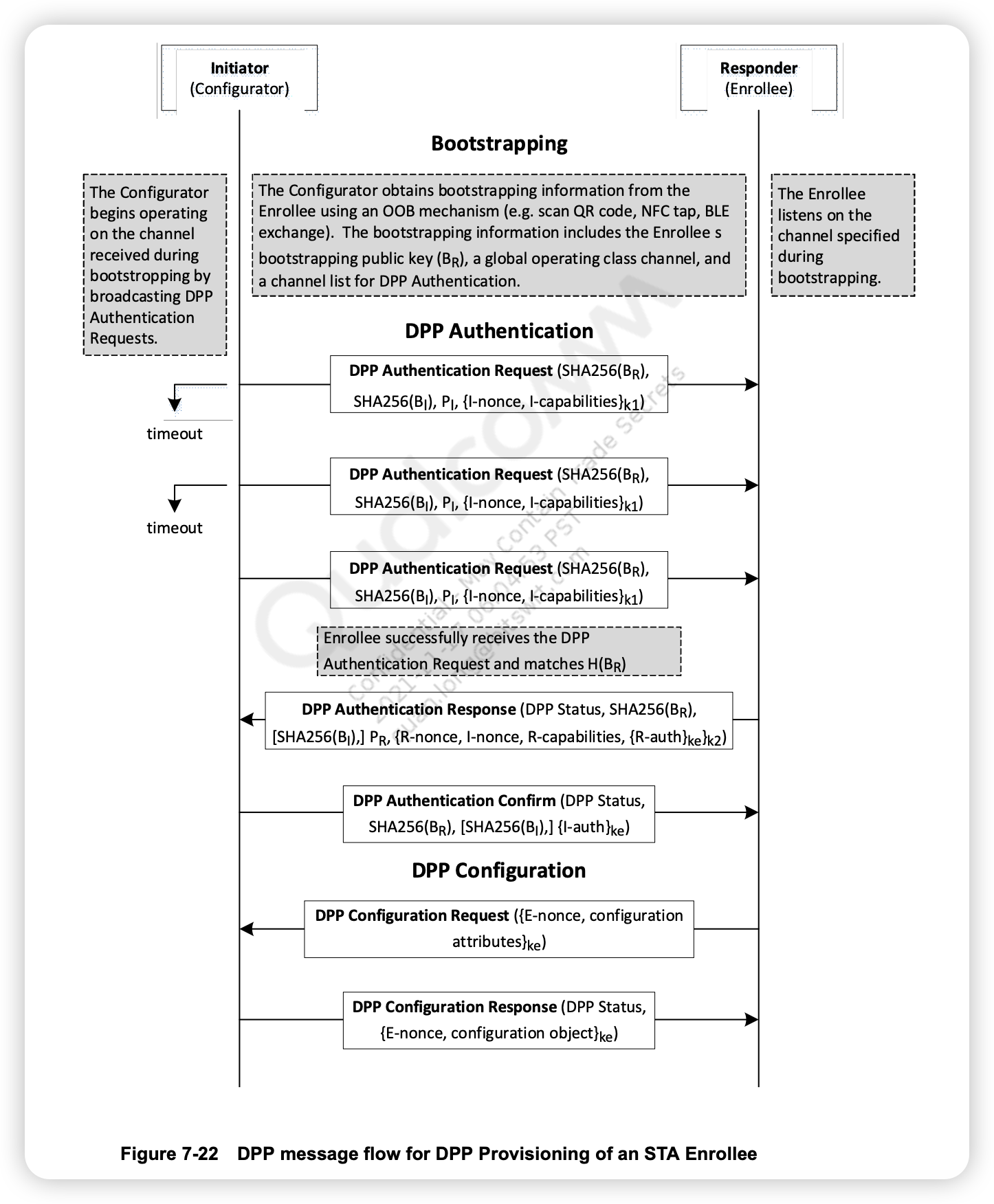
- The DPP Authentication protocol requires either the Enrollee or the Configurator to take on the role of Initiator. In the example message flow shown in the following figure, the Configurator takes on the role of Initiator and obtains bootstrapping information for the Enrollee. The bootstrapping information includes the public bootstrap key as well as a Global Operating Class and a Channel Number list that the STA Enrollee listens on to perform the DPP authentication protocol.
- The Initiator issues DPP Authentication Request frames on channels in the channel list and waits for a response from the Responder. After successfully receiving a response, the Initiator validates the result and transmits a DPP Authentication Confirm frame to complete DPP Authentication. After successful completion of these frame exchanges, a secure channel between the Initiator/Configurator and Responder/Enrollee is established.
- The STA Enrollee initiates the provisioning phase by transmitting a DPP Configuration Request frame, and is provisioned with configuration information in a DPP Configuration Response frame. After successfully receiving the DPP Configuration Response frame, the Enrollee is provisioned with the information required to establish secure access to the AP.
- If the STA Enrollee is provisioned with a Connector as credentials, it discovers the AP, transmits a Peer Discovery Request frame and then waits for a Peer Discovery Response frame. Upon successful validation of the Peer Discovery frames, the STA and AP mutually derive a PMK and PMKID, and the STA follows the standard IEEE 802.11 procedures.
- Alternatively, if the STA Enrollee is provisioned with PSK or PSK Passphrase credentials to allow it to connect to a legacy AP, the STA Enrollee will use the configuration to discover and associate to an AP using IEEE 802.11 and WPA2-Personal network access procedures.