Contents
21.1.5 NAWDS
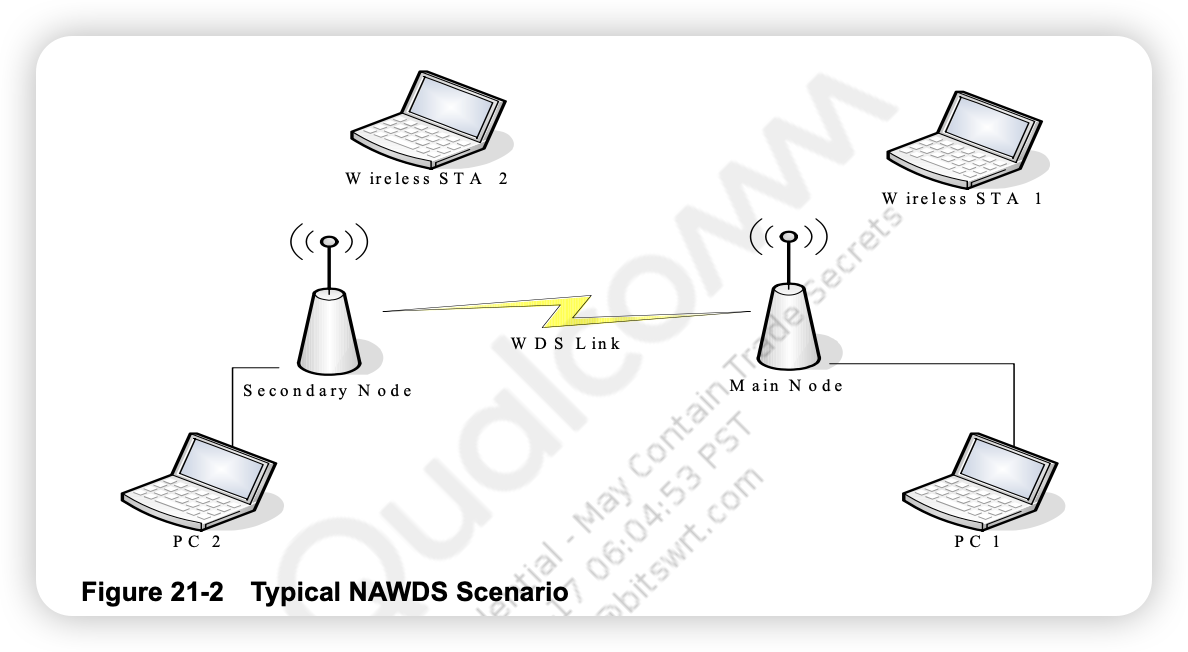
The Non-Association WDS (NAWDS) is an AP feature that provides an alternative WDS solution that does not require any association between peer NAWDS APs. A NAWDS AP could be statically configured to receive WDS packets from and send packets to peer NAWDS APs. With the learning feature enabled, a NAWDS AP would learn the MAC address automatically to perform WDS. Figure 21-2 is a typical NAWDS scenario where main node and secondary node is the NAWDS AP.
NOTE: If a NAWDS link breaks, it is necessary to add the peer again, although the peer entry is already available in the NAWDS table. For example, if the cfg80211tool ath0 vht_ 11ng 1 command is issued to enable 256QAM, the NAWDS link breaks. In this scenario, the entry must be added again to the table for NAWDS to work.
Terminology
-
NAWDS Non-Association WDS. In contrast with the association-based WDS, the NAWDS link is established without the necessity of going through the 802.11 association process.
-
NAWDS AP A NAWDS AP is an AP with the NAWDS feature enabled that supports WDS 4-address communication. Depending on sending a beacon or not, a NAWDS AP could be either a NAWDS Repeater or a NAWDS Bridge.
-
NAWDS Repeater A NAWDS Repeater sends out beacons and supports IEEE802.11 association process which allows STA connecting to it. The STAs and PCs which associate/connect to the repeater could reach other STAs/PCs in peer NAWDS AP via NAWDS link.
-
NAWDS Bridge A NAWDS bridge does NOT send out beacons. The PCs which connect to the bridge could reach other STAs/PCs in peer NAWDS AP via NAWDS link.
-
Static NAWDS Repeater/Bridge A static NAWDS AP does NOT have learning function. Users have to manually add the MAC address of a peer NAWDS AP into its NAWDS MAC table so that it can communicate with other NAWDS APs. If the MAC address of a NAWDS AP is not in the NAWDS MAC table, a static NAWDS AP would drop packets from that particular NAWDS AP.
-
Learning NAWDS Repeater/Bridge A learning NAWDS AP has a learning function. Whenever it receives packets from peer NAWDS AP, it would learn the MAC address of the peer AP and add the address to its NAWDS MAC table so that it could further communicate with the particular AP through NAWDS link.
21.1.5.1 NAWDS overview
WDS to NAWDS
The existing WDS solution builds a WDS tree to forward frames and is association-based. The original WDS design could be depicted as in Figure 21-3.
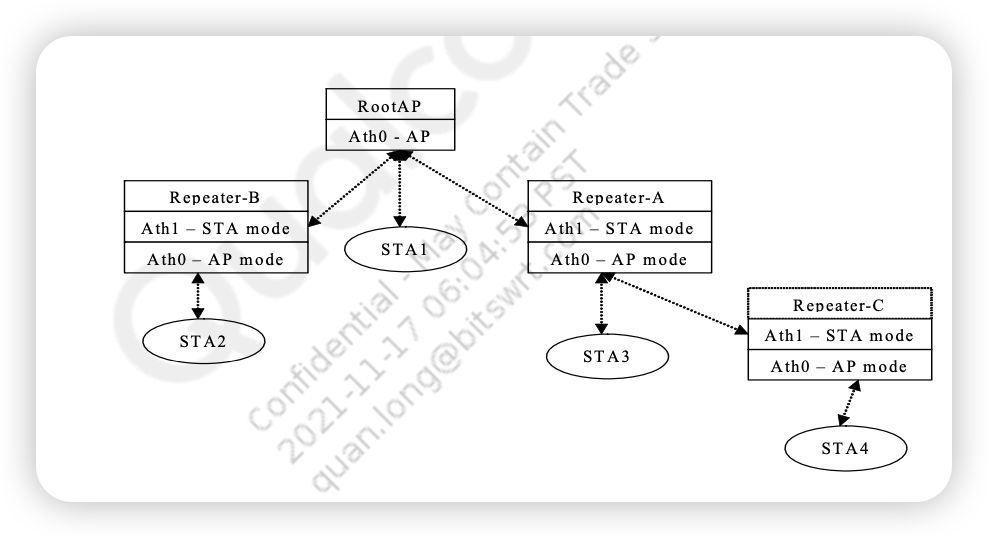
Figure 21-3 Typical WDS Block Diagram NAWDS is more like a flat structure which means that any NAWDS node directly talks to one or multiple NAWDS peers. Users could either configure the MAC addresses of the peer NAWDS APs for each NAWDS AP or enable the learning feature to allow the NAWDS AP to add the MAC addresses of the peer NAWDS AP automatically when it get packets from peer APs.
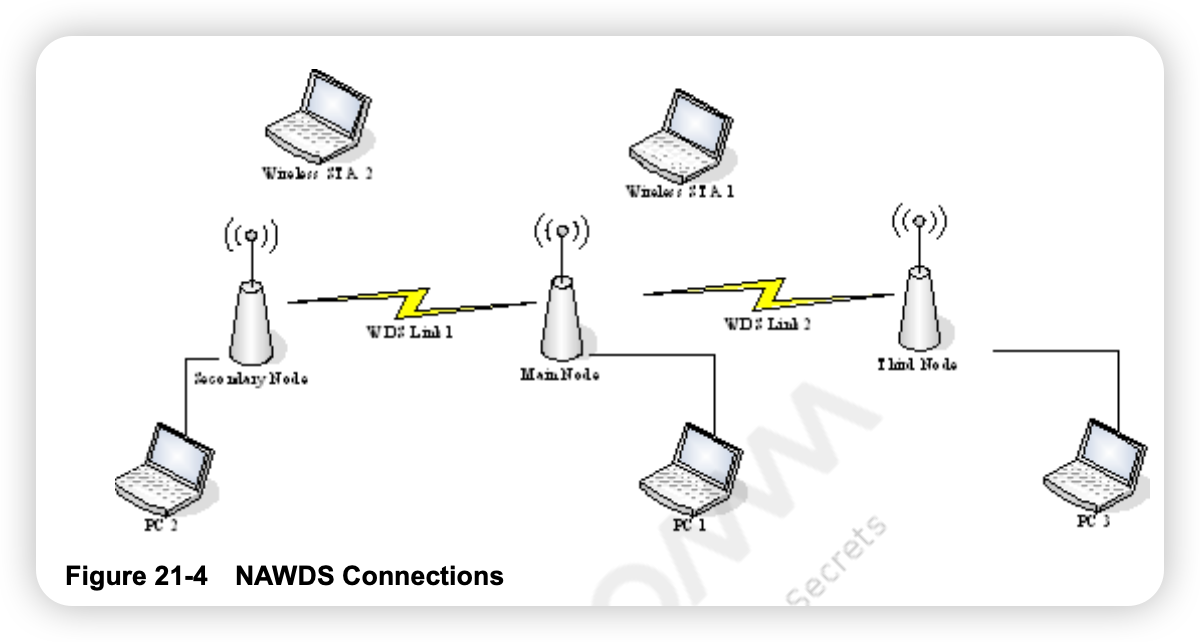
Figure 21-4 NAWDS Connections Due to the nature of NAWDS, some constraints are applied to the feature:
- It is necessary to have at least one static node. Other nodes know peer NAWDS nodes either by learning or by statically configuring.
- Between any two NAWDS nodes, frames must use four addresses for proper forwarding.
- All the NAWDS nodes in the network must have the same encryption setting. Currently only Open/WEP mode is supported.
- Since there is no association process, the capability of peer NAWDS AP must be configured in advanced.
